Ever had a rotten tooth pulled? I have, and it smarts a bit. But would I rather that tooth was still there, or that it abscessed and dumped toxins into my bloodstream? Not really. And that’s essentially the case in favor of docking most lambs’ tails shortly after birth.
“But Bill!” you protest. “A lamb’s tail is natural, and your rotten tooth was the product of years of bad human decision-making — namely your decisions to eat chocolate and not floss often enough.”

Actually the lamb’s tail is just as unnatural as a rotten tooth. We put it there, millennia ago. Shortly after humans domesticated sheep, we started to choose ones with long, fat tails because we liked eating fat in those days.
As with nearly everything that we have done to alter animals through selective breeding, we took it a little too far, and arrived at the point where the vast majority of sheep cannot lift the full length of their tails. Then we bred sheep to have wool rather than hair. Wool is much more absorbent than hair, which is mostly self-cleaning. As a result, there’s a constant risk that the wool on the tail can become soiled with urine and dung and remain moist. This creates the perfect breeding ground for flies.

Unlike any other domesticated livestock — cattle, goats, buffalo, you name it — we created a set of conditions that put sheep at increased risk of infestation by blowflies by making its tail so heavy that it can’t lift it out of the way of its elimination and then covering it with wool that will hold onto any liquid waste that hits it. It’s our responsibility to protect them from the selection choices that our ancestors made that put them at risk. That means docking most sheep.
What it does not mean is cutting off the tail just behind the ears. Docking a lamb’s tail too short is probably worse than not docking it at all. It increases the risk of rectal and vaginal prolapses, and leaves the bare skin around the anus and vulva exposed to the elements.
And it also doesn’t mean waiting until it’s a month or two old and amputating the tail without anesthetic.
Most hair sheep can be left undocked, and some of the Scandinavian and dairy breeds have naturally short tails that don’t really need docking. But the vast majority of sheep do need it.
Those who oppose docking also say we should simply breed for sheep with short tails. But if you have been breeding animals for very long, you know that the more traits you’re selecting for simultaneously, the slower your progress is on any single trait. And if you select for any single trait, you lose progress on others.
Personally, I don’t want sheep with short tails that are poor mothers, don’t grow well, have poor muscling, are more susceptible to parasitism, require birthing assistance, and have a low quality wool clip. (These are just a few of the traits that most shepherds are selecting for that would have to be de-emphasized in the name of selection for short tails.)
They also say that tail docking causes pain and increases risk of rectal and vaginal prolapse, and while it’s true that some methods of docking have these faults, it’s entirely possible to dock a lamb’s tail with minimal pain and with virtually no risk of rectal or vaginal prolapse.

A Humane Docking Protocol
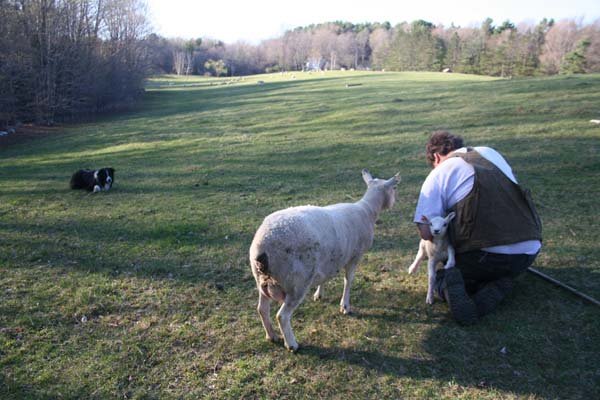
For more than 25 years, I have used rubber rings to dock lambs tails. I adopted this tool because it was one that I could use single-handed and very quickly. Many other methods require two people (one holding the lamb and another performing the procedure), and are very slow (a hot iron takes a few minutes to heat up between lambs).
I do this procedure when the lamb is still very young — usually less than 24 hours old. I wait until the lamb has had a good feeding, and I try to make sure the bond between mother and lamb is strong.

The latest veterinary guidance is to apply the ring at the distal end of the caudal fold. I find the point on the underside of the tail where the bare skin ends, and I apply the band there. This leaves a tail that is slightly longer than the distal end of the caudal fold, and can be more easily located by feel.
Most importantly, it leaves all of the musculature that is involved in tail mobility in place. Sheep docked this way easily raise their tails to urinate and defecate. They can flick their tails from side to side to shoo flies away, and the bare skin on their nether regions is entirely covered.

This procedure leaves lambs with a tail that will be four to six inches long in the adult sheep. Some people who are accustomed to looking at show sheep call it a pump handle. They can laugh all they want, but I’ve raised more than 10,000 lambs and have never had a single rectal prolapse. I’ve never had a ewe that I raised myself have a vaginal prolapse.
There’s no doubt that a lamb, even a little one, feels some pain when you apply a rubber ring to its tail. But it doesn’t last long, and the only pain behavior they usually display is a rapid flicking of the tail. Most of the time, they’re nursing again before I get the instrument back in the pocket of my equipment vest.

When compared with the discomfort of lugging around a fat, sodden tail that no longer serves its intended purpose and that may become the source of blowfly infestation that can lead to septicemia and death, those few minutes of discomfort wouldn’t bother me if I had to switch places with the lamb.



From what I have read about domesticated animal selection, traits often come “bundled.” For example, there is the decades-old Russian research on foxes selected only for their docility that then began to show a collection of other traits–color variations including spots, floppier ears, etc. So long tails in modern sheep breeds most likely came with other traits humans selected for (fleece quality, longer breeding periods, twinning, etc.). There was an attempt (in the 1950s, 1960s?), to breed a tail-less Dorset (from one naturally born without a tail), but it failed and the research was abandoned.
This is probably the best article I have ever read on tail docking. Nice to see some logic applied to this practice. Thanks!
Hi Oogie,
I think many of the primitive British breeds like yours, Shetlands, Scottish blackface, and even the Swaledales, etc., got less selection pressure for the fat tail and more for survivability. Generally speaking, these are probably more similar to some of the Scandinavian breeds, having come over with the Norsemen.
There are plenty of hill, fell, and mountain sheep flocks in the UK that do not dock tails. They usually use the primitive breeds. They also enjoy a climate that’s a little less favorable to blowflies than what we usually see in the humid regions of the US. They have our humidity for sure, but fewer hot days when blowfly populations really explode. And of course, the hill flocks are at elevations where the temperatures are even cooler than the arable land, and where there’s a nearly constant wind.
Unless you have a breed where it is mandatory to not dock tails. Black Welsh Mountain sheep with docked tails are unregistered unless there is a specific veterinary reason that it was required for a specific individual animal. Routine docking of tails will result in your expulsion from the registry and you will be forbidden from ever owning registered sheep again.
However, there is a reason, Black Welsh do not get the manure build up of other breeds. In 21 years of raising them I have had a grand total of 1 animal who built up manure on the long tail and got fly strike. She was treated and then her and her offspring were all culled. That was early on in our breeding of these sheep and I’ve never had another one since then.
Fly strike resistance is a breed trait that must be preserved and part of that is letting the sheep potentially develop manure build up and using that as a culling criteria.
Comments are closed.